Studies on temperature dependant inductance characteristics of Planar MLI
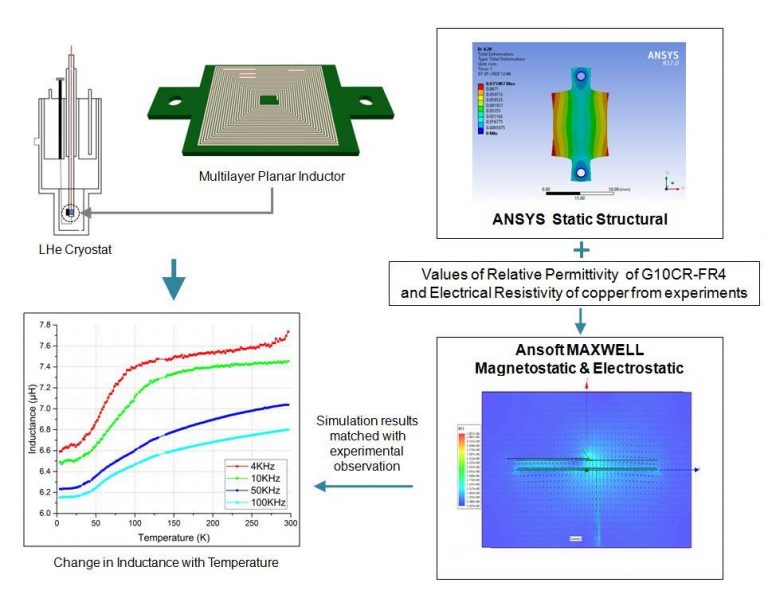
Investigation on the temperature dependence characteristics of cryogenic planar Multi-Layer Inductor (MLI) is presented here. It was found that the inductance of a planar MLI at a specific frequency varies with temperature when the sensor is cooled down to 4.2 K. Detailed analysis of various factors that contribute to the variation in the sensor performance are considered and its effects on the inductance value were verified using a combination of experiments and simulations. A novel approach was adopted in the investigation of the effects of thermal deformations on the sensor, by calculating the inter layer capacitance. Relative permittivity of the base material (G10CR-FR4) at cryogenic temperatures were obtained through experiments. ANSYS Static Structural package was used for modeling thermally induced deformations and the capacitance, inductance values of these thermally deformed geometries were obtained using Ansoft MAXWELL. From the analysis, it was found that the variation in the inductance of the sensor has a direct correlation with the electrical resistivity (and hence RRR) of the coil material which is not obvious from inductance models. The number of inductor layers and the area of component layer can also contribute to the temperature dependence phenomenon.
List of publications related to this work
- Pankaj Sagar, Harris K Hassan, E. D. A. Lakshmi, Kashif Akber, Girish P. S., Abhay Singh Gour, R Karunanithi. Investigation on Temperature Dependent Inductance (TDI) of a Planar Multi-Layer Inductor (MLI) down to 4.2 K. Review Of Scientific Instruments, 91(9):726–738, 2020.